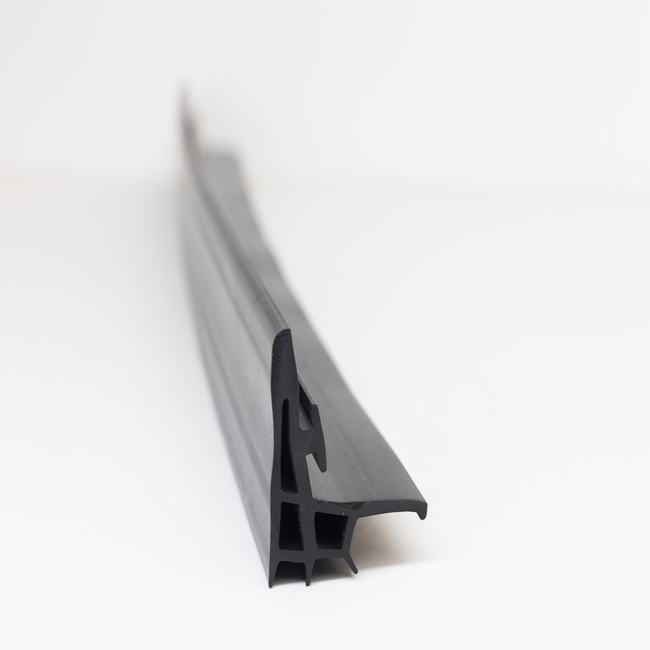
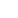
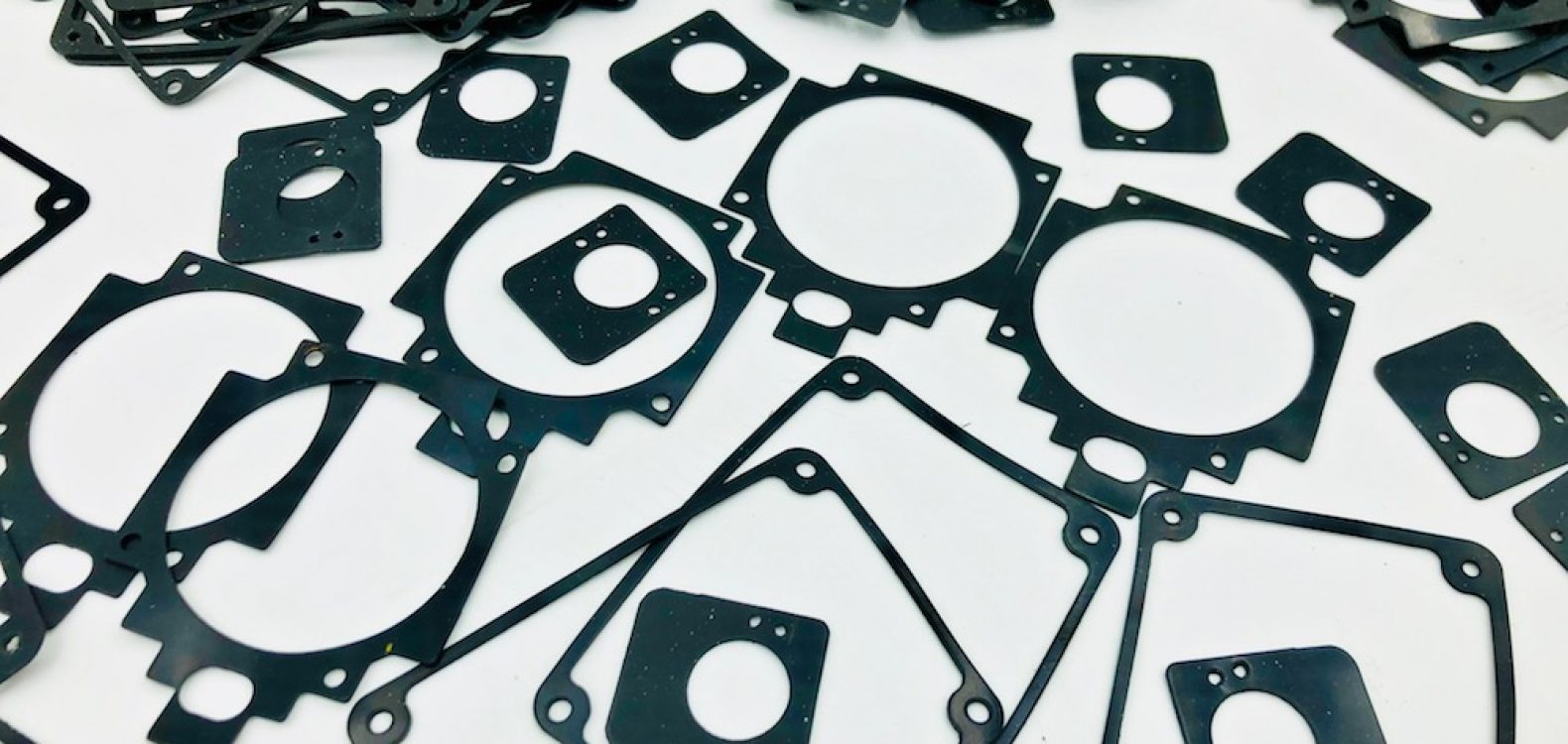
A dilatation seal, also known as an expansion joint or expansion seal, is a specialized engineering component designed to accommodate thermal expansion, contraction, vibration, and movement in various structures and systems. These seals are commonly used in construction, civil engineering, industrial applications, and infrastructure projects to ensure the structural integrity and longevity of a wide range of structures, such as buildings, bridges, pipelines, roads, and more. This very long description provides a comprehensive overview of dilatation seals, including their functions, types, materials, applications, and benefits.
Functions of Dilatation Seals:
- Compensating for Thermal Expansion and Contraction: One of the primary functions of dilatation seals is to compensate for the expansion and contraction of materials due to temperature variations. When temperature changes occur, materials tend to expand when heated and contract when cooled. This can exert considerable stress on structures, which dilatation seals help to alleviate.
- Absorbing Vibration and Movement: Dilatation seals are also used to absorb and dissipate vibrations and movements caused by factors like seismic activity, machinery operation, traffic loads, and settling of buildings. By doing so, they prevent the transfer of these forces to the connected components of a structure.
- Sealing Gaps and Joints: Dilatation seals are essential for sealing the gaps and joints between different structural elements, preventing the ingress of moisture, contaminants, and other environmental factors. This helps protect the structural integrity and longevity of the components and the overall structure.
Types of Dilatation Seals:
There are several types of dilatation seals, each designed to address specific engineering requirements:
- Compression Seals: These seals are designed to compress and expand to accommodate movement and are commonly used in bridges and roadways.
- Expansion Joints: Expansion joints are used to absorb expansion and contraction in structures like buildings and bridges. They can be of various designs, including sliding, hinge, and modular types.
- Pipe Expansion Joints: These are used in pipelines to accommodate thermal expansion, contraction, and movement while maintaining a leak-proof seal.
- Strip Seals: Strip seals are often used in bridge expansion joints and consist of a series of metal strips or plates that can flex to accommodate movement.
- Modular Seals: These are pre-engineered, modular units that can be customized for specific applications and are commonly used in large infrastructure projects.
Materials Used in Dilatation Seals:
Dilatation seals can be constructed from various materials, depending on the application. Common materials include:
- Rubber: Natural rubber or synthetic elastomers are often used for their flexibility and durability.
- Metal: Stainless steel, aluminum, or other metals provide strength and stability in high-stress environments.
- Neoprene: Neoprene rubber is a popular choice due to its resistance to weathering and chemicals.
- Fabric-Reinforced Elastomers: These materials combine the flexibility of rubber with the strength of fabric reinforcement, making them suitable for heavy-duty applications.
Applications of Dilatation Seals:
Dilatation seals find application in a wide range of industries and structures, including:
- Bridges: Expansion joints in bridges accommodate movement, prevent damage, and extend the lifespan of the structure.
- Buildings: Dilatation seals are used in commercial and residential buildings to prevent damage from temperature changes and settling.
- Pipelines: Pipe expansion joints protect pipelines from thermal expansion and contraction, as well as ground movement.
- Roads and Highways: Expansion joints in roadways ensure a smooth and safe driving surface.
- Industrial Plants: These seals are used in industrial environments to prevent damage to structures and equipment due to vibration and thermal expansion.
Benefits of Dilatation Seals:
- Structural Integrity: Dilatation seals help maintain the structural integrity of various components and systems, extending their lifespan.
- Safety: In transportation infrastructure, such as bridges and roads, dilatation seals improve safety by reducing the risk of accidents and damage.
- Cost Savings: By preventing structural damage and the need for frequent repairs, dilatation seals can lead to significant cost savings over time.
- Environmental Protection: Sealing gaps and joints with dilatation seals helps protect structures from moisture infiltration and environmental damage.
In summary, dilatation seals are crucial components in many construction and engineering projects, enabling structures to withstand thermal fluctuations, movements, and vibrations while maintaining their structural integrity and safety. The choice of seal type and material depends on the specific requirements of each application, making dilatation seals a versatile and essential element in modern engineering and infrastructure.