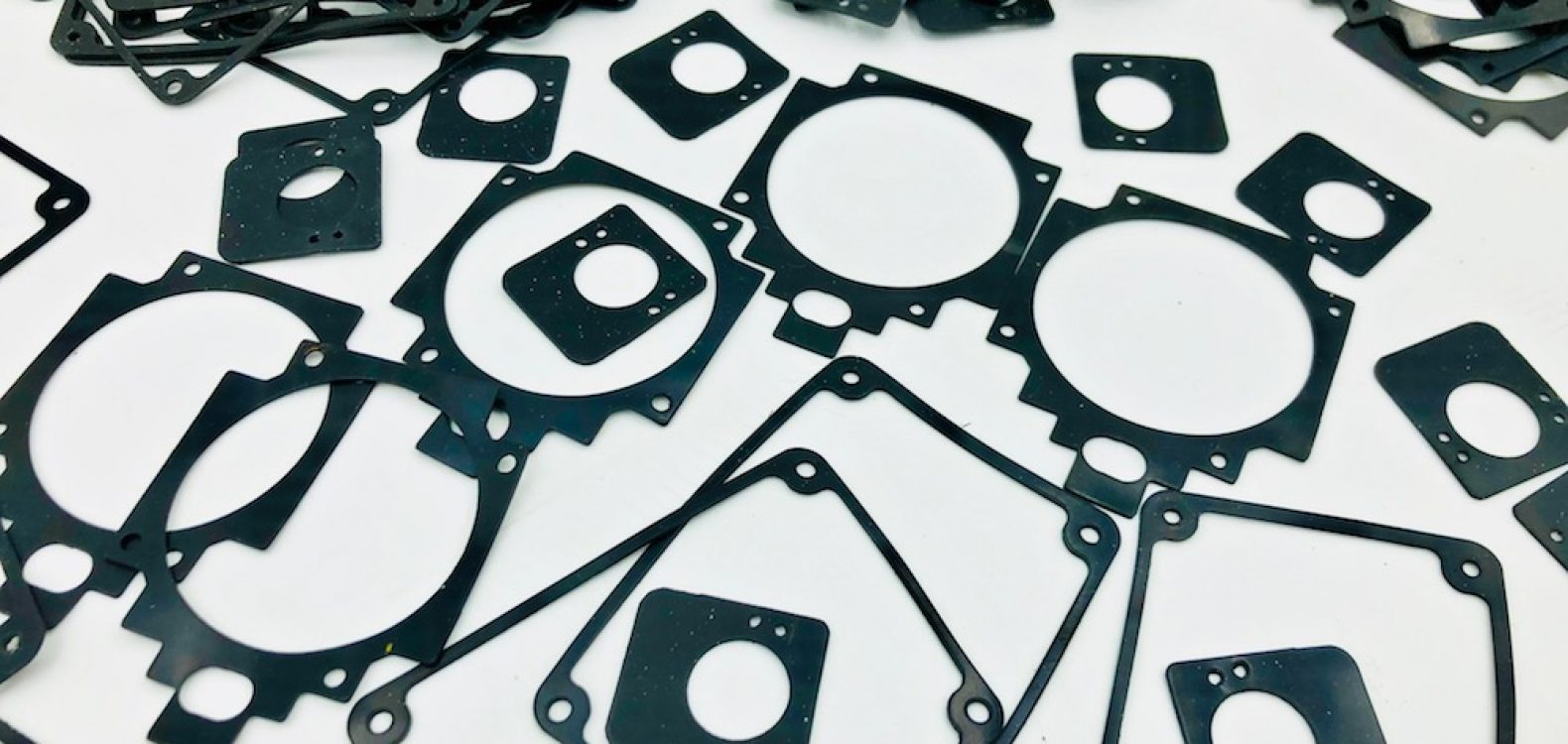
Industrial seals are critical components used in various industries to prevent the escape or ingress of fluids, gases, contaminants, and particles within mechanical systems and equipment. These seals play a pivotal role in maintaining the efficiency, safety, and reliability of industrial processes. This comprehensive description covers the functions, types, materials, applications, and benefits of industrial seals.
Functions of Industrial Seals:
- Leakage Prevention: The primary function of industrial seals is to create a barrier that prevents the unwanted escape of fluids or gases, such as oil, water, air, chemicals, or gases, from a system or the entry of contaminants or environmental elements into the system. This is crucial for maintaining operational efficiency and environmental safety.
- Friction Reduction: Some industrial seals, like gaskets and O-rings, reduce friction between moving parts, leading to improved performance and reduced wear and tear.
- Vibration Dampening: Seals can also absorb and dampen vibrations in rotating or reciprocating equipment, reducing noise and prolonging equipment life.
- Pressure Regulation: Seals play a role in maintaining the desired pressure levels within a system, ensuring that it operates within specified tolerances.
Types of Industrial Seals:
There are various types of industrial seals, each designed for specific applications and conditions. Common types include:
- Gaskets: These flat or shaped seals are placed between two mating surfaces to prevent leakage. They are commonly used in flanged connections, such as in pipelines, valves, and pumps.
- O-Rings: O-rings are circular seals typically made of rubber or elastomeric materials. They are used in dynamic and static applications and provide effective sealing for hydraulic and pneumatic systems.
- Mechanical Seals: Mechanical seals are used in rotating equipment, like pumps and compressors, to prevent leakage along the shaft. They consist of stationary and rotating components with a sealing face.
- Lip Seals: Lip seals, also known as oil seals, are used to retain lubricants and exclude contaminants in rotary shaft applications. They consist of a flexible lip that contacts the shaft.
- Hydraulic Seals: Hydraulic seals are designed for hydraulic systems and prevent the escape of hydraulic fluids. They include rod seals, piston seals, and wipers, each serving a specific purpose.
- Pneumatic Seals: These seals are used in pneumatic systems to prevent air leakage. They include rod seals, piston seals, and other designs tailored to pneumatic applications.
- Diaphragm Seals: Diaphragm seals are flexible barriers that separate process fluids from measurement instruments. They are commonly used in pressure and temperature measurement applications.
Materials Used in Industrial Seals:
Industrial seals can be made from a variety of materials, depending on the application requirements. Common seal materials include:
- Elastomers: Rubber materials such as Nitrile, Viton, EPDM, and Silicone are commonly used for their flexibility and resistance to various fluids and temperatures.
- Metal: Metals like stainless steel, bronze, and aluminum are used for mechanical seals and high-temperature applications.
- Plastics: Materials like PTFE (Teflon) and polyurethane are used in applications that require chemical resistance and low friction.
- Composite Materials: Some seals are made from composite materials that combine the advantages of both rubber and metal, offering flexibility and strength.
Applications of Industrial Seals:
Industrial seals are used across a wide range of industries and applications, including:
- Oil and Gas: Seals are essential in pipelines, valves, pumps, and drilling equipment to prevent leakage and ensure safe operations.
- Automotive: Gaskets, O-rings, and lip seals are used in engines, transmissions, and hydraulic systems.
- Aerospace: Aerospace applications rely on seals in hydraulic systems, engines, and critical components to maintain the integrity of the aircraft.
- Chemical Processing: Seals are used in reactors, valves, and pumps to prevent leaks of hazardous chemicals and maintain process control.
- Food and Pharmaceutical: Seals in food and pharmaceutical manufacturing equipment ensure product safety and compliance with hygiene standards.
- Power Generation: Seals are used in turbines, generators, and heat exchangers to maintain operational efficiency and prevent energy losses.
Benefits of Industrial Seals:
The use of industrial seals provides several key advantages:
- Leakage Prevention: Seals ensure the containment of fluids and gases, preventing leaks that can lead to safety hazards, environmental damage, and operational inefficiencies.
- Equipment Longevity: By reducing friction, dampening vibrations, and preventing contamination, seals extend the lifespan of industrial equipment and reduce maintenance costs.
- Operational Efficiency: Seals contribute to improved operational efficiency by maintaining pressure, temperature, and fluid control within systems.
- Safety and Environmental Compliance: Seals help maintain the safety of industrial processes and ensure compliance with environmental regulations.
- Reduced Downtime: Properly selected and maintained seals minimize unplanned downtime, contributing to increased productivity.
In conclusion, industrial seals are indispensable components in a wide range of industrial applications, where their function as barriers to leakage, friction reducers, and vibration dampeners contributes to the overall efficiency, safety, and reliability of industrial processes and equipment. The selection of the appropriate seal type and material is crucial to ensuring optimal performance in each specific application.